Proven Finite Element Tools for Geomagic Design -
A full-featured, simulation solution for linear static and eigenvalue analysis.
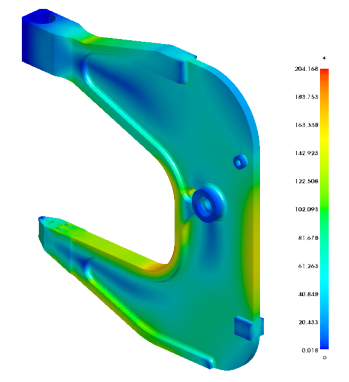
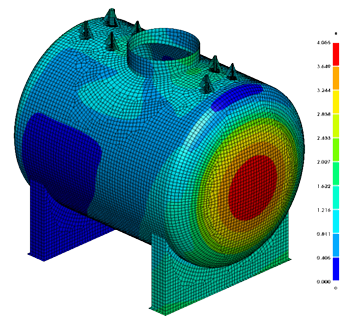
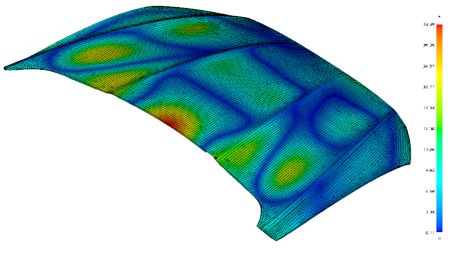
PreSys and NISA, advanced finite element analysis tools, are now combined for use by Geomagic users. This full-featured package allows users to automatically convert Geomagic CAD data into finite element models, define material and loading constraints and perform a design simulation. This type of analysis allows engineers to identify potential problems and improve product designs, reducing product development time and cost, while improving performance.
PreSys, a Pre/Post-Processor with a strong heritage, allows the user to create even the most complex finite element models easily. It is a full-featured, core solution that can be used on its own or with a variety of available add-on applications. The system offers advanced automeshing tools to provide the highest quality mesh with little CAD data preparation on imported or created geometries. All required analysis data can be created via intuitive forms.
The solver engine, NISA is one of the most comprehensive engineering analysis suites available and has been an engineer’s favorite for more than 40 years. It is capable of extremely accurate linear static and eigenvalue analyses.
Features:
- An Intuitive, Customizable GUI
- High Performance Graphics
- A Scripting Interface
- A Tree Structure Layout for Model Data
- Easy Import/Export of Geomagic Design Data
- Complete Post Processing of Simulation Results
Linear Static Analysis
Static Analysis Features:
- Selection of Efficient Solvers
- Buckling Analysis
- Interia Relief
- Rigid Links & MPC
- Interlaminar Shear & Edge Effects for Composite Elements
- Multiple Load Cases
Material Properties
- Isotropic or Orthotropic, Temperature Dependent
- Layer & Sandwich Composite Material
- Various Composite Failure Criteria
Boundary Conditions
- Specified Nodal Displacement (Zero/Non-zero; Translation or Rotation)
- Coupled Displacement; Multipoint Constraints
- Concentrated Force, Moment, Pressure Load, Thermal Load
- Gravity, Linear/Angular Acceleration
- Moving Load
Printed & Graphical Output
- Displacements, Stresses & Strains at Elements & Nodes
- Principle Stresses & Their Directions
- Von Mises, Maximum Shear & Octahedral Shear Stresses
- Averaged & Unaveraged Nodal Stresses, Element Stresses at Gauss Points & Centroid
- Buckling Load Forms & Mode Shapes
Linear Dynamic Analysis
Eigenvalue Analysis
- Natural Frequencies, Mode Shapes
- Modal Stresses & Strain Energy
- Multiple Eigenvalue Extraction Algorithms
- Extraction of Zero Frequencies (Rigid Body Modes) & Coincident Frequencies
Modal Dynamic Analysis
- Viscous, Structural, Proportional & Material Damping
- Capabilities to Handle Rigid Body Modes
- Transient Dynamic Analysis
- Time Dependent Ground Excitations, Nodal Forces & Pressure Loading
- Nonzero Initial Displacements
- Time History & Snapshot Output for Results
- Generation of Floor Response Spectra
- Frequency Response Analysis
- Frequency Dependent Harmonic Ground Excitation, Nodal Force & Pressure Loading
- Point-to-point Transfer Function Calculation
- Random Vibration Analysis
- Stationary & Non-stationary Input
- Auto PSD & Complex Cross PSD Input
- Numerical or Exact Integration of the PSDs to Compute the Covariance Matrices
- PSD & RMS Response Output
- Shock (Response) Spectrum Analysis (Seismic)
- Multi-directional Displacement, Velocity or Acceleration Spectra Input
- Modal Combination Rules
- Absolute Sum
- Square Root of Sum of Square or RMS Sum
- Peak RMS or NRL Sum
- Complete Quadratic Combination (CQC) Sum
- Automated Mode Selection & Spectra Computation by U.S. Navy DDAM Method
- Missing Mass Correction